The Remarkable Ecological Zones of California
California is a state known for its diverse natural landscapes, ranging from lush forests to expansive deserts. One of the most fascinating aspects of California’s natural environment is the presence of unique ecological zones, particularly in its desert regions. These ecological zones are characterized by distinct plant and animal communities that have adapted to the harsh california desert conditions. In this article, we will explore some of California’s remarkable desert ecological zones and the diverse life forms that call them home.
The Mojave Desert
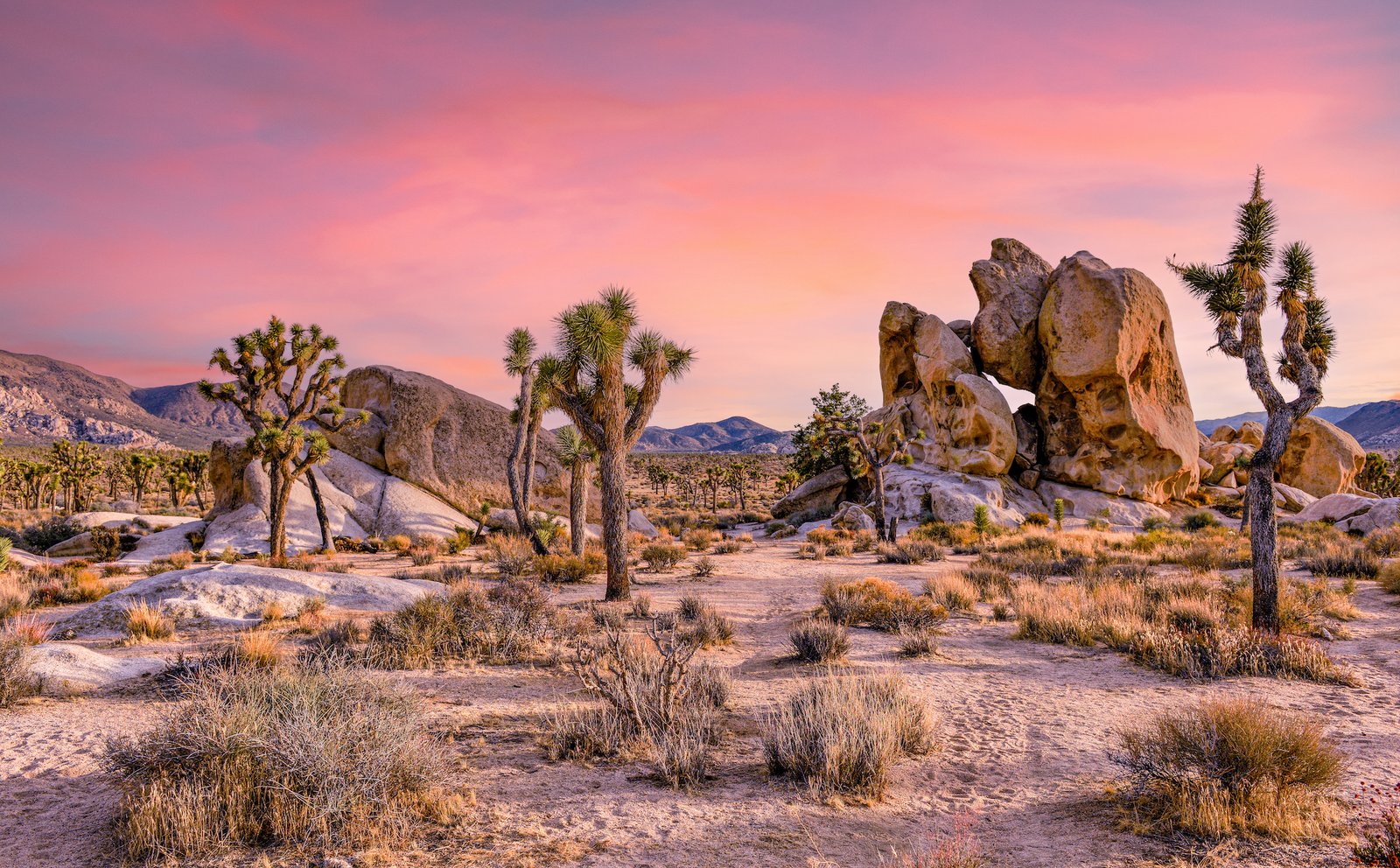
The Mojave Desert is one of California’s most iconic desert landscapes. Spanning across parts of southern California, Nevada, Utah, and Arizona, the Mojave Desert is characterized by its vast stretches of arid land, rocky mountains, and Joshua trees. Despite the harsh conditions, the Mojave Desert is home to a surprising variety of plant and animal species. Some notable inhabitants of the Mojave Desert include the desert tortoise, the kit fox, and the iconic Joshua tree. The desert’s unique geological formations, such as the famous Joshua Tree National Park, attract visitors from all over the world.
The Colorado Desert
The Colorado Desert, also known as the Low Desert, is located in southeastern California and extends into parts of Arizona and Mexico. This desert region is characterized by its lower elevation and higher temperatures compared to the Mojave Desert. The Colorado Desert is home to a diverse range of plant species, including the iconic California fan palm and the desert ironwood. It is also known for its unique geological features, such as the Salton Sea, a large inland saline lake that supports a variety of bird species.
The Great Basin Desert
The Great Basin Desert is located in eastern California, encompassing parts of Nevada, Utah, and Oregon. Unlike the other desert regions in California, the Great Basin Desert experiences colder temperatures and receives more precipitation. This unique combination of factors allows for the presence of diverse plant and animal species. The Great Basin Desert is home to sagebrush, aspen groves, and a variety of small mammals such as jackrabbits and coyotes. It is also known for its stunning mountain ranges, including the Sierra Nevada and the White Mountains.
Preserving California’s Desert Diversity
California’s desert ecological zones are not only fascinating from a scientific perspective but also play a crucial role in the state’s ecosystem. These unique environments provide habitat for numerous plant and animal species, some of which are found nowhere else in the world. However, desert ecosystems face numerous threats, including habitat loss, climate change, and invasive species.
To preserve the diversity of California’s desert regions, various conservation efforts are underway. National parks, wildlife refuges, and other protected areas help safeguard the fragile desert ecosystems and provide opportunities for research, education, and recreation. Additionally, organizations and individuals are working together to promote sustainable practices and raise awareness about the importance of desert conservation.
By understanding and appreciating the unique ecological zones in California’s deserts, we can contribute to their preservation and ensure that future generations can continue to marvel at the remarkable diversity found in these arid landscapes.
Conclusion
California’s desert regions are home to a remarkable diversity of ecological zones, each with its own unique plant and animal communities. From the iconic Joshua trees of the Mojave Desert to the majestic mountain ranges of the Great Basin Desert, these desert ecosystems offer a glimpse into the resilience and adaptability of life in extreme conditions. By appreciating and protecting these fragile environments, we can ensure that California’s desert diversity continues to thrive for generations to come.