Exploring the Lunar Surface: The Chang’e-6 Mission
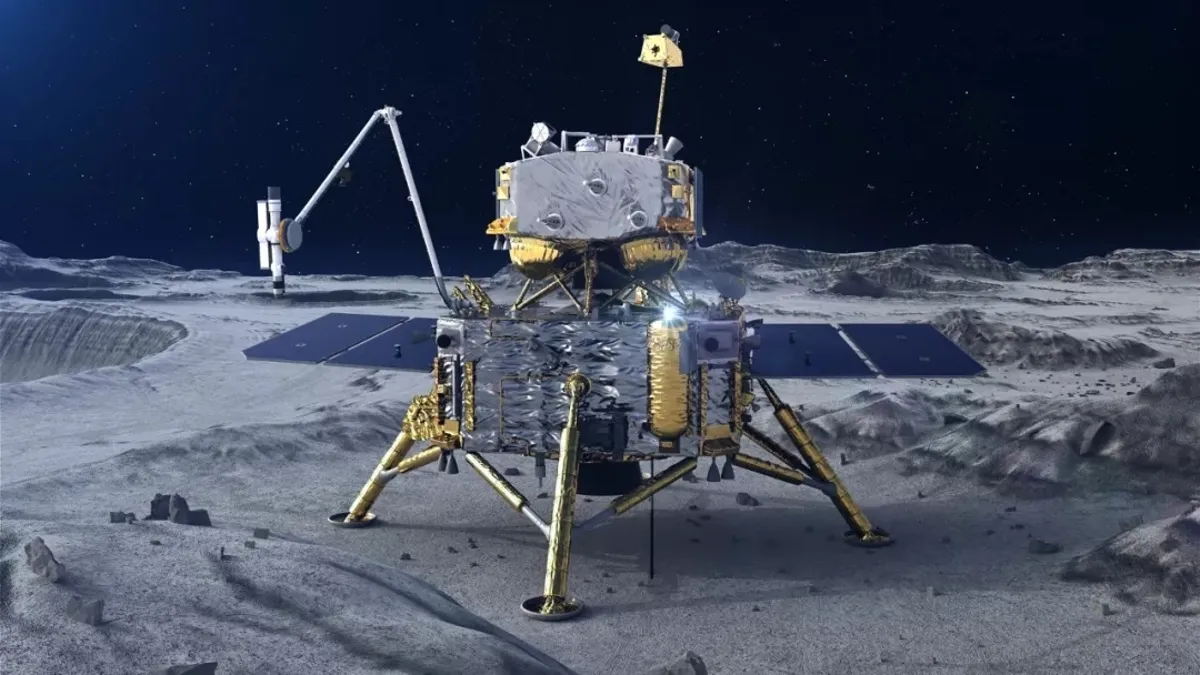
China’s Chang’e-6 lunar probe has completed its mission on the moon’s surface and is now en route back to Earth. This ambitious endeavor marks another milestone in China’s space exploration efforts, as the probe collected soil and rock samples during its time on the lunar surface. However, the mission raises questions about whether its objectives are purely scientific or if political motivations also play a role.
Scientific Endeavor: Advancing Lunar Exploration
At its core, the Chang’e-6 mission represents a significant scientific endeavor aimed at advancing our understanding of the moon and its geological composition. By collecting soil and rock samples from different locations on the lunar surface, scientists hope to gain insights into the moon’s formation, evolution, and geology. These samples will be analyzed in laboratories on Earth, providing valuable data for lunar research and future space exploration missions.
Political Implications: China’s Space Ambitions
While the Chang’e-6 mission is driven by scientific objectives, it also carries political significance, reflecting China’s ambitions to establish itself as a major player in space exploration. China has made substantial investments in its space program in recent years, launching a series of successful missions to the moon, Mars, and beyond. The Chang’e-6 mission serves as a demonstration of China’s technological prowess and its growing capabilities in space exploration.
Competition in Space: Geopolitical Dynamics
The pursuit of space exploration is not solely driven by scientific curiosity but is also influenced by geopolitical dynamics and national interests. China’s space ambitions are viewed within the context of an increasingly competitive global space race, with countries vying for strategic advantage and prestige in space exploration. As China asserts its presence in space, it challenges the traditional dominance of space powers like the United States and Russia, shaping the geopolitical landscape of the 21st century.
International Collaboration: Balancing Cooperation and Competition
Despite geopolitical tensions, there are also opportunities for international collaboration in space exploration. China has expressed openness to collaboration with other countries and space agencies, including joint missions and data sharing initiatives. However, geopolitical rivalries and concerns over technology transfer have hindered deeper cooperation between China and Western space powers. Finding a balance between competition and collaboration will be crucial in advancing humanity’s collective exploration of space.
Space Diplomacy: Building Alliances in the Cosmos
Space exploration has emerged as a new frontier for diplomacy, with countries using their space programs to foster diplomatic relations and build alliances. China’s space ambitions are intertwined with its broader geopolitical goals, as it seeks to strengthen its influence and soft power on the world stage. By showcasing its technological achievements and collaborating with other countries in space exploration, China aims to enhance its global standing and shape the future of space governance.
Ethical Considerations: Environmental and Cultural Preservation
As humanity ventures further into space, ethical considerations surrounding environmental and cultural preservation become increasingly important. The moon and other celestial bodies are not just scientific resources but also hold cultural and historical significance for humanity. As China conducts missions like Chang’e-6, it must prioritize responsible stewardship of the lunar environment and respect the cultural heritage of the sites it explores.
Looking to the Future: Humanity’s Journey Beyond Earth
As China’s Chang’e-6 mission returns to Earth with its precious cargo of lunar samples, it heralds a new chapter in humanity’s journey of exploration and discovery. The data gathered from these samples will deepen our understanding of the moon’s origins and evolution, paving the way for future lunar missions and potentially even human settlement. As nations continue to push the boundaries of space exploration, collaboration, innovation, and responsible stewardship will be key to unlocking the mysteries of the cosmos for generations to come.