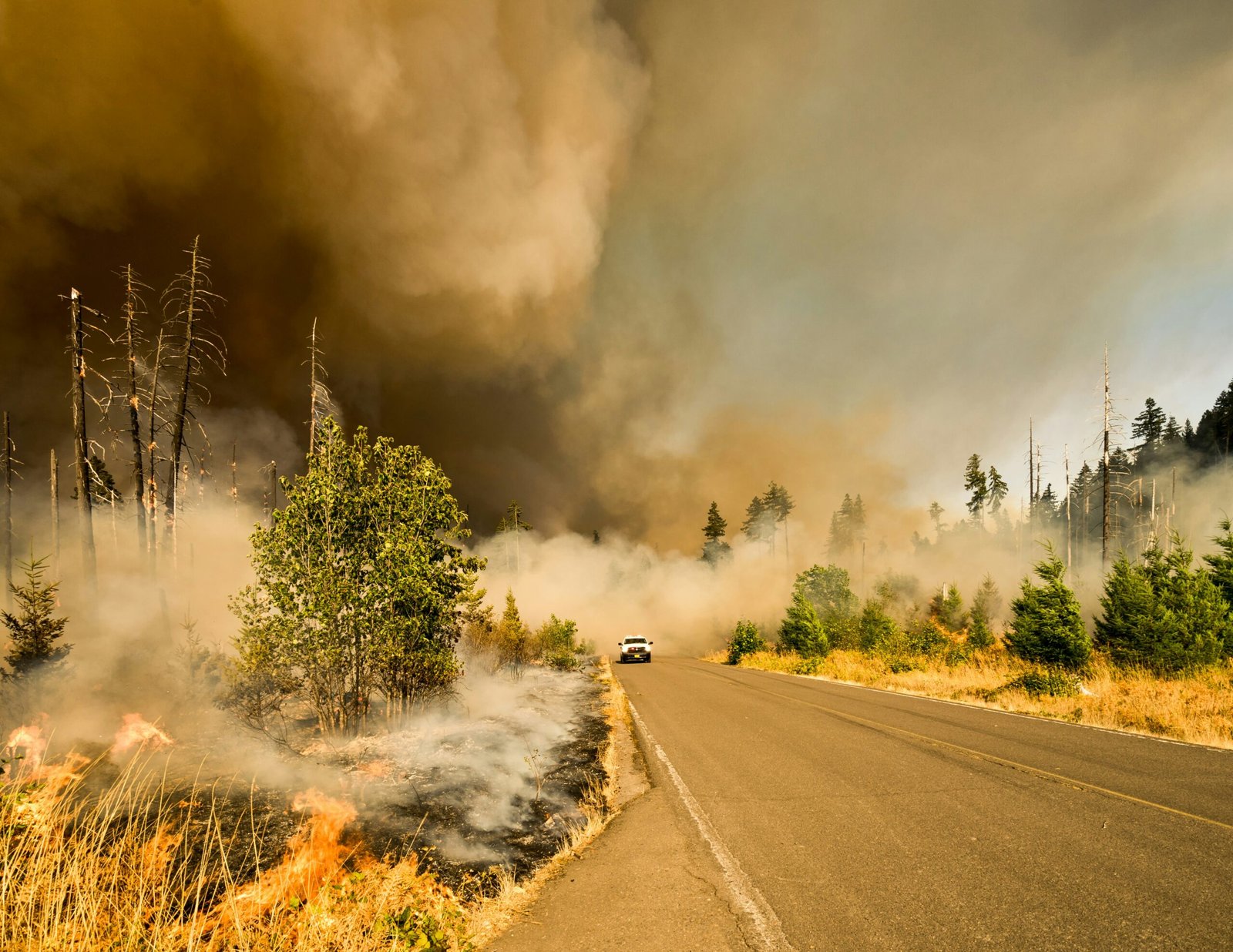
Wildfires have become an increasingly concerning issue in California, with devastating consequences for both the environment and human lives. In recent years, the state has been actively exploring new strategies and technologies to prevent and manage these wildfires. From innovative forest management practices to the use of fire-resistant construction materials, California is taking proactive steps to mitigate the risks associated with wildfires.
1. Forest Management Practices
One of the key areas of focus in wildfire prevention is forest management. California has been investing in forest thinning and prescribed burns as part of its strategy to reduce fuel loads and prevent the rapid spread of wildfires. Forest thinning involves selectively removing trees and vegetation to create spacing between them, reducing the density of the forest and decreasing the risk of wildfires.
Prescribed burns, on the other hand, involve intentionally setting controlled fires under specific weather conditions to reduce the accumulation of flammable materials in the forest. By removing dry brush and dead trees, these burns help to create firebreaks and prevent the spread of wildfires.
2. Fire-Resistant Construction Materials
Another important aspect of wildfire prevention is the use of fire-resistant construction materials. In areas prone to wildfires, building structures with materials that are resistant to ignition can significantly reduce the risk of property damage and loss. California has been promoting the use of fire-resistant materials, such as fire-resistant roofing, siding, and windows, in new construction and retrofitting existing buildings.
Fire-resistant roofing materials, for example, are designed to withstand the radiant heat from wildfires and prevent the ignition of the building. These materials are typically made of non-combustible materials, such as metal, concrete, or clay tiles.
In addition to fire-resistant materials, California has also implemented building codes and regulations that require the use of fire-resistant designs and construction techniques. This includes the installation of ember-resistant vents, which prevent embers from entering the building and igniting flammable materials.
3. Early Warning Systems
Early warning systems play a crucial role in wildfire management. California has been investing in advanced technology and infrastructure to improve early detection and response to wildfires. This includes the deployment of remote sensors, weather monitoring stations, and satellite imagery to detect and track wildfires in real-time.
These early warning systems provide valuable information to firefighters and emergency responders, enabling them to quickly assess the situation and deploy resources effectively. In some cases, these systems can even trigger automated alerts to residents in affected areas, allowing them to evacuate safely and minimize the risk to human lives.
4. Community Preparedness and Education
California recognizes the importance of community preparedness and education in wildfire prevention and management. The state has been actively promoting public awareness campaigns, community training programs, and educational initiatives to inform residents about wildfire risks and the necessary steps to protect themselves and their properties.
These initiatives include providing resources and guidelines on creating defensible spaces around homes, developing evacuation plans, and conducting drills to ensure that communities are well-prepared in the event of a wildfire. By empowering residents with knowledge and resources, California aims to reduce the impact of wildfires and enhance community resilience.
5. Collaborative Efforts and Research
Addressing the complex issue of wildfires requires collaborative efforts and ongoing research. California has been actively collaborating with federal agencies, research institutions, and other stakeholders to develop innovative solutions and improve wildfire prevention and management strategies.
Research initiatives are focused on understanding the behavior of wildfires, studying the impact of climate change on fire patterns, and developing new technologies to enhance early detection and response. These efforts aim to continuously improve the state’s ability to prevent, manage, and mitigate the risks associated with wildfires.
In conclusion, California is taking proactive steps to prevent and manage wildfires by implementing various strategies and technologies. From forest management practices to the use of fire-resistant construction materials, the state is committed to reducing the risks associated with wildfires. By investing in early warning systems, community preparedness, and collaborative research, California is paving the way for a more resilient and fire-safe future.