Introduction
California has been at the forefront of renewable energy growth in the United States. With its commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to a clean energy future, the state has made significant strides in increasing its renewable energy capacity. This blog post provides an overview of the renewable energy growth in California, highlighting key initiatives, policies, and achievements.
Renewable Energy Targets
California has set ambitious renewable energy targets to drive its transition to a low-carbon economy. The state aims to generate 100% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2045. To achieve this goal, California has implemented various policies and programs to incentivize renewable energy development and deployment.
Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS)
The Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS) is one of the key policies driving renewable energy growth in California. It requires utilities in the state to procure a certain percentage of their electricity from eligible renewable energy sources. The RPS targets have been progressively increased over the years, with the current target set at 60% by 2030.
Solar Power
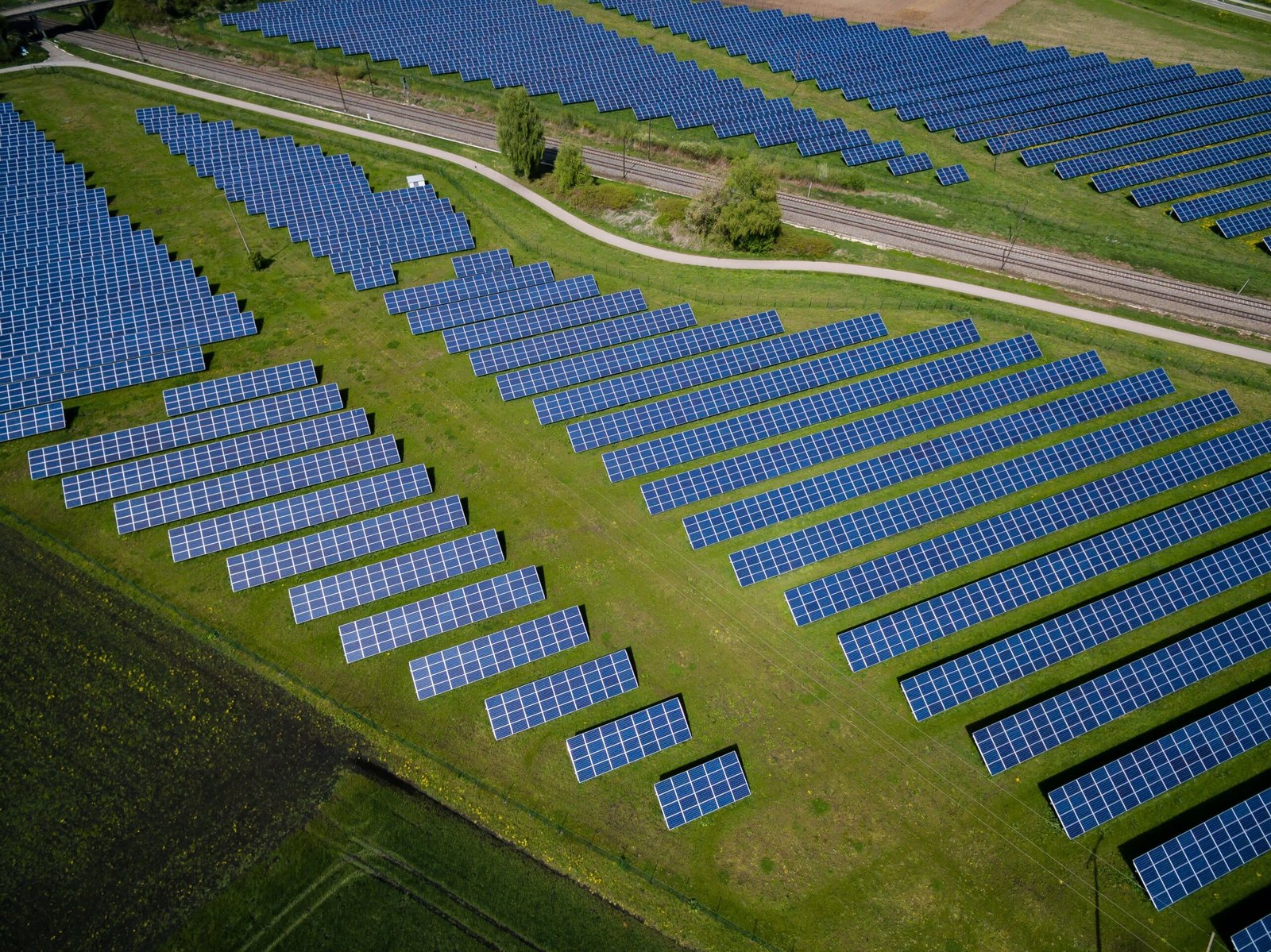
Solar power has been a major contributor to the renewable energy growth in California. The state has abundant sunshine, making it an ideal location for solar energy generation. California leads the nation in solar capacity, with numerous large-scale solar farms and rooftop solar installations. The California Solar Initiative, along with various tax incentives and rebate programs, has played a significant role in promoting solar power adoption.
Wind Power
Wind power is another important component of California’s renewable energy portfolio. The state has favorable wind resources, particularly along its coastline and in mountainous regions. California ranks among the top states in terms of installed wind capacity. The development of wind farms, both onshore and offshore, has been facilitated by policies such as the Renewable Energy Transmission Initiative and the Wind Energy Planning Area.
Geothermal Energy
California is home to some of the largest geothermal power plants in the world. Geothermal energy utilizes heat from the Earth’s core to generate electricity. The state’s geothermal resources, primarily located in the Imperial Valley and the Geysers region, have been harnessed for clean energy production. The California Geothermal Resources Act and the Renewable Energy Transmission Initiative have supported the development of geothermal projects.
Energy Storage
As renewable energy capacity continues to grow, energy storage plays a crucial role in ensuring grid reliability and stability. California has been a pioneer in advancing energy storage technologies and deployment. The state has set a target of 1.3 gigawatts of energy storage by 2024. Initiatives like the Self-Generation Incentive Program and the Energy Storage Procurement Framework have encouraged the adoption of energy storage systems.
Benefits of Renewable Energy
The growth of renewable energy in California brings numerous benefits to the state and its residents. It reduces greenhouse gas emissions, improves air quality, and mitigates the impacts of climate change. Renewable energy projects also create jobs, stimulate economic growth, and enhance energy security. Furthermore, renewable energy diversifies the state’s energy sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting a sustainable energy future.
Conclusion
California’s commitment to renewable energy growth has positioned the state as a leader in the clean energy transition. Through ambitious targets, supportive policies, and innovative programs, California continues to expand its renewable energy capacity. The growth of solar power, wind power, geothermal energy, and energy storage has paved the way for a greener and more sustainable future. As the state progresses towards its goal of 100% renewable electricity, California serves as a model for other regions seeking to embrace renewable energy and combat climate change.